Embedded software developer
Who is an Embedded software developer?
embedded software developer with linux kernel skills primary purpose is to write software that allows hardware features on a variety of products, from mobile devices such as phones and laptops to complicated machines used throughout the healthcare, aerospace, and financial sectors. Embedded programmers execute scripts and programs that make devices work as expected in a multitude of sectors. Embedded developers write programmes for use in a range of sectors, ranging from new communication to shipping, security, and medical environments, because more and more devices use incorporated or embedded computer applications. Usually, embedded developers use the programming languages C and C++. As embedded developers work with groups including hardware engineers, industrial sector, and user interface and expertise specialists to ensure that software or hardware teams work seamlessly effectively and efficiently, this task involves a lot of teamwork.
Figure. 1
Are you looking for a embedded software developer with linux kernel skills. Get in touch we can help with your requirements.
How to improve skills ?
Begin to have code analysis
Code reviews are among the most productive ways to mitigate bugs in an embedded device, and code reviews are amongst the things that developers do most with their hands. The fact is there is no such thing as a flawless programmer but it is not only that feedback can easily spot bugs, it is also a fantastic place to learn more embedded knowledge and enhance positive input from your colleagues.
Skills in Master Debugger
The personal opinion might be to master abilities that avoid glitches in a process, but defects can occur regardless of how perfect a developer or team might be. It is important that groups master significantly reduces the risk methods and monitoring strategies as well. Questionnaires of embedded systems indicate that typical developers spend 40% of the period debugging, equivalent to almost 5 months in a single year! For any development team to maximise their design process, the poisonous tree fruit is to avoid errors and practice the tools necessary to quickly identify the ones who make it through. Reducing debugging time from 40 percent to 30 percent will save 6 weeks of development effort per developer, which can make sense to price, reliability and functionality, maybe not in development costs.
Start to Automate Testing
A long, repetitive and error prone method is manual checking software. Any extra software or alteration could result in the need to go away and reapply the whole system to make sure that nothing has been broken by the update. Lots of research may also involve regular framework. It is needed to execute test automation and other software testing; current software development processes combine automated tests and configuration management servers. While these procedures may take time to set up, they offer a way to enhance the consistency of code in the broader system and shorten the length and labour expended on testing. Test driven development proponents may point to all sorts of fascinating figures about how essential it is to build the test case first and then write the code that actually allows the study pass. I’ve never completely accepted TDD personally, but I’ve realized that it helped develop my own programme by following many of its principles, such as streamlining data sets and worrying about the case study first.
Different questions about applications
There are main features and design trends that lead to customer-facing features of a product. Rather than redefining the wheel, impact on aquatic and reusing such features would allow developers to concentrate on the value-added features and recycle everyone else. Within the code base, or perhaps notably, in the software architecture, portability and reuse both begin with distinguishing software issues. Current code bases are also closely coupled or may have poor cohesion so in the same software modules, different features are all implemented. The development of new cohesive groups and close to the bottom-coupling modules would increase the replication and functionality of code and will also make things easier for developers to manage and expand the code.
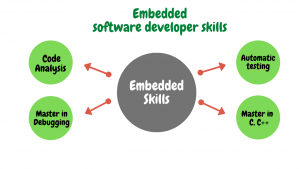
Figure. 2
What are Duties and obligations of an Embedded Developer?
Collect Functional criteria
Embedded developers obtain specifications and measurements from customers, professional developers, and production teams before starting development work. Usually, these specifications include descriptions of anticipated software output and use scenarios, along with parallelization and bandwidth standards. Embedded developers convert these into requirements that direct development research after collecting these specifications.
Code Creation and Writing
An embedded developer’s central task is to write tools to facilitate hardware features on a wide variety of products, from devices such as mobile phones and smartphones to complicated equipment used for the medical, transport, and defence industries. This aspect of the position involves familiarity with a broad range of programming philosophies as well as the capacity to comprehend how hardware function is assisted by software.
Regression testing and upgrading behaviour
Embedded developers perform frequent preventive maintenance and debugging tasks during the design and development phase to ensure that their code performs as planned. This may involve both analysing the quality of large-scale applications and collaborating with smaller software components to address performance problems such as time delay and accidents. In fact, the embedded developer engages in operations of continuous delivery.
Maintain documents for projects
For any applications they operate on, embedded developers often maintain comprehensive, accurate records. This may include examples of particular codes and modules, failure and bug information, and specification and requirements-related documents. In order to help potential developers, embedded do something that their documents comply with best practises and provide detailed details on actions taken during testing and development. To exchange code and eradicate bugs, they also implement accurate continuous integration standards.
Collaborating with teams for design and development
Embedded developers work more closely with a variety of teams when writing applications, like user interface and user experience (UI / UX) developers, quality control teams, and professional developers, to ensure that the software system of the systems function properly. New specifications that include updating or customising code to correct and make corrections that did not occur in previous versions will often be uncovered by this partnership.
Improve the performance and consistency of systems
Embedded developers continually work to improve their programmes’ performance, performance, and scalability. In particular this includes involving more effective solutions by streamlining codes and components in order to accomplish the same objectives in a shorter period of time, but it may also involve getting improvements to how software communicates with the hardware in order to improve stability and minimise failure rates.
Read more about this.